Application whitelisting is a method for security control which only allows approved processes,
applications and DLLs to load and execute. It involves building a baseline of known trusted applications that are approved to use and updating this baseline when an application is changed or added.
Whitelisting is useful in environments that don’t change very often, can delay or interfere with attackers’ actions; however, it can be bypassed by attackers
and cannot serve as the standalone measure for security.
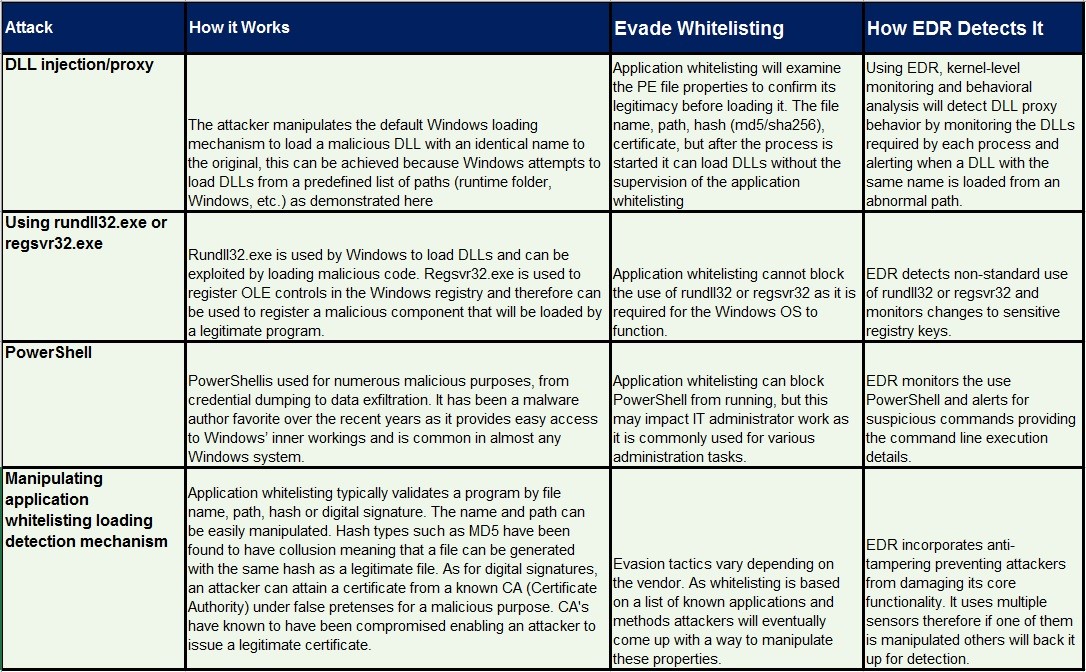
4 ways malware bypasses whitelisting
(Source: Cyberbit EDR – Kernel-based Endpoint Detection vs. Whitelisting)
Prevention is Insufficient, Detection is Required
In the article Prevention Is Futile in 2020 Gartner urges organizations to shift from a preventive security approach to an approach that focuses on protecting Information via pervasive monitoring and collective intelligence. While whitelisting can certainly reduce the noise of traditional attacks, in the current threat landscape, there is no security measure which can protect against every attack, therefore good detection is critical for when prevention fails.
Download FREE whitepaper: Cyberbit EDR Kernel-Based Endpoint Detection vs. Whitelisting
Additional Resources
• Bypassing Application Whitelisting – CERT CC Blog
• Bypassing Whitelisting – Github
• Cansecwest – bypassing McCafee whitelisting
Tal Morgenstern is EDR Product Architect at Cyberbit

