A new strain of the Petya ransomware is spreading rapidly over the last 24 hours. The new variant attacked critical infrastructure, airports, pharmaceutical companies, and public transit companies throughout Europe, Asia, and North America. This post will provide a brief overview of the old and new tactics used by the new Petya, and a comprehensive list of recommendations.
[this post was updated on 6/29/2017 with new tips and IOCs]
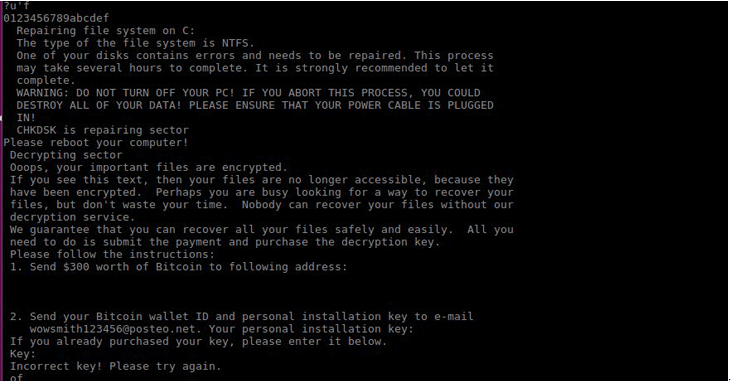
What’s Old
The Petya ransomware strain spreads using the exact same MS17-010 SMBv1 vulnerability exploit called EternalBlue, allegedly an NSA hack, which was also used in the recent WannaCry attack.
What’s New
While the propagation method was used by WannaCry, Petya is a much more violent form of ransomware. Unlike WannaCry which encrypts the user’s hard drive, Petya attacks the MBR – the low-level Master Boot Record and creates its own boot loader.
Petya implements new killer features for lateral movement:
- Using the remote administration tool “psexec”, which executes it on the remote host:
psexec –accepteula -s -d c:\windows\system32\rundll32.exe “C:\Windows\<filename>\,#1″ - Using the Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) Command-line tool:
c:\windows\system32\wbem\wmic.exe /node:”<node>” /user:”<user>” /password:”<password>” process call create “C:\Windows\System32\rundll32.exe “C:\Windows\<file>\” #1
Another notable difference between Petya and WannaCry is that it initially infects via a malicious Word document. The document is sent as an attachment to a phishing email and exploits a known Office vulnerability: CVE-2017-0199 which enables remote code execution. Once the attachment is opened the malware is downloaded through an embedded link.
Cyberbit EDR and Petya
Customers using Cyberbit Endpoint Detection and Response are protected against Petya. The attack is detected immediately during infection by the EDR’s behavioral analysis, as well as during encryption and propagation. According to VirusTotal only 13 vendors identify the new Petya Ransomware strain. It is therefore essential to complement antivirus with an endpoint detection and response solution, which uses behavioral analysis in addition to signature lists and detects attacks which are not identified by antivirus systems.
What you should do
- Patch Microsoft Office to prevent infection via Microsoft Word attachments – install the CVE-2017-0199 update to patch Microsoft Office/WordPad Remote Code Execution Vulnerability.
- Patch Windows Workstations: if you have not done that after the WannaCry attack install the SMBv1 patch now in order to prevent the attack from spreading.
- Disable shutdown via command line: disable the option to use cmd /k shutdown -a. This command is used by the malware to initially shut down the computer, after which the computer will boot from the new malware boot loader.
- Don’t pay: we do not advise paying the ransom as files are unlikely to be decrypted after you pay
- Shut Down: when you suspect that you have been infected, shut down your computer immediately, DO NOT REBOOT, and ask an IT expert for help
- Remove admin rights for standard users
- Vaccinate: use this vaccination script, however, use it with caution as vaccines may be detected by security software and blocked.
IOCs:
Search for these IOCs:
Hashes:
MD5
- 0df7179693755b810403a972f4466afb
- 42b2ff216d14c2c8387c8eabfb1ab7d0
- 71b6a493388e7d0b40c83ce903bc6b04
- e285b6ce047015943e685e6638bd837e
- e595c02185d8e12be347915865270cca
- 9B853B8FE232B8DED38355513CFD4F30
- CBB9927813FA027AC12D7388720D4771
SHA1
- 34f917aaba5684fbe56d3c57d48ef2a1aa7cf06d
- 9717cfdc2d023812dbc84a941674eb23a2a8ef06
- 38e2855e11e353cedf9a8a4f2f2747f1c5c07fcf
- 56c03d8e43f50568741704aee482704a4f5005ad
- a809a63bc5e31670ff117d838522dec433f74bee
- bec678164cedea578a7aff4589018fa41551c27f
- d5bf3f100e7dbcc434d7c58ebf64052329a60fc2
- aba7aa41057c8a6b184ba5776c20f7e8fc97c657
- 0ff07caedad54c9b65e5873ac2d81b3126754aac
- 51eafbb626103765d3aedfd098b94d0e77de1196
- 078de2dc59ce59f503c63bd61f1ef8353dc7cf5f
- 7ca37b86f4acc702f108449c391dd2485b5ca18c
- 2bc182f04b935c7e358ed9c9e6df09ae6af47168
- 1b83c00143a1bb2bf16b46c01f36d53fb66f82b5
- 82920a2ad0138a2a8efc744ae5849c6dde6b435d
SHA256
- 22053C34DCD54A5E3C2C9344AB47349A702B8CFDB5796F876AEE1B075A670926
- 1FE78C7159DBCB3F59FF8D410BD9191868DEA1B01EE3ECCD82BCC34A416895B5
- EEF090314FBEC77B20E2470A8318FC288B2DE19A23D069FE049F0D519D901B95
- 027cc450ef5f8c5f653329641ec1fed91f694e0d229928963b30f6b0d7d3a745
- eae9771e2eeb7ea3c6059485da39e77b8c0c369232f01334954fbac1c186c998
IPs:
- 95.141.115.108
- 185.165.29.78
- 84.200.16.242
- 111.90.139.247
Emails:
- wowsmith123456@posteo.net
- iva76y3pr@outlook.com // by WhiteWolfCyber
- carmellar4hegp@outlook.com // by WhiteWolfCyber
- amanda44i8sq@outlook.com // by WhiteWolfCyber
- gabrielai59bjg@outlook.com
- christagcimrl@outlook.com
- amparoy982wa@outlook.com
- rachael052bx@outlook.com
- sybilm0gdwc@outlook.com
- christian.malcharzik@gmail.com
Who Was Infected:
As of today, these organizations are known to be infected:
- The Ukrainian Government: https://twitter.com/RozenkoPavlo/status/879677026256510976
- Russian oil giant Rosneft: https://twitter.com/RosneftRu/status/879665160012673024
- Rotterdam Port: https://twitter.com/OpiniePaultje/status/879680984219779072
- Targets in spain: http://www.elconfidencial.com/tecnologia/2017-06-27/ataque-ransomware-dla-piper-wannacry_1405839/
- Maersk: https://twitter.com/campuscodi/status/879712143133872132
- Retailer in Kharkov, Ukraine: https://twitter.com/golub/status/879707965179088896
- Ukraine ATM: https://twitter.com/mikko/status/879735944907296768
- WPP: https://twitter.com/WPP/status/879706256612761600
- Pharma giant Merck: https://twitter.com/JackPosobiec/status/879734999196602369
- Kiev Metro Station: https://ain.ua/2017/06/27/kievenergo-i-ukrainskie-banki-podverglis-xakerskoj-atake
- Saint-Gobain: https://twitter.com/AnimalDubz/status/879684389860454402
- Mars, Nivea, and Auchan offices in the Ukraine: https://www.buro247.ru/technology/news/27-jun-2017-petya-wannacry.html
- Chernobyl’s Nuclear Plan Radiation Monitoring: http://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/europe/chernobyl-ukraine-petya-cyber-attack-hack-nuclear-power-plant-danger-latest-a7810941.html
For more information on how to remain protected contact info@cyberbit.com

